The medical devices market in Ethiopia is on the rise, driven by different factors. A growing population, increasing prevalence of chronic and infectious diseases, and increased healthcare expenditure are key contributors to the rise of medical device market opportunities in Ethiopia. The government’s commitment to improving healthcare infrastructure and access, together with increasing private sector investment, is further fueling market growth presenting significant opportunities for both domestic and international manufacturers.
Ethiopia is one of the most preferred countries in Africa to be considered as the top entry point to African market by medical device manufacturers and suppliers. Some clear points why manufacturers are choosing Ethiopia to break the medical device market in the continent are discussed in the following sections.
- Promising government plans and policies
Ethiopia’s journey towards economic prosperity and improved healthcare has been marked by significant progress in recent years. With the goal of attaining middle-income status, the Government of Ethiopia introduced the ambitious 10 Years Perspective Plan from 2020/2021 to 2029/2030 (source- ministry of planning and development). This plan underscores the government’s commitment to achieving universal health coverage (UHC) and meeting the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) to enhance the well-being of its population. In situational descriptions of its preceding development plans, this specific Ten years development plan identified particular challenges in some sectors where the government did not ensure sustainability of the previously planned growth.
In chapter seven of this plan document that provided objectives for demography and human resource development, it sets clear goals to be achieved in the healthcare system. These includes-building an effective health system based on prevention and control methods; to mitigate maternal and child mortalities; to prevent communicable and noncommunicable diseases that may cause death or illness; to protect citizens from fatal health incidents. For achieving these objectives, there were many targets planned to be met by the ended of 2030- used to indicate the sector’s performance and significantly improve public health outcomes, some of which are-
- Strengthening reproductive health:
- Increase access to family planning services to reduce population growth.
- Decrease maternal mortality rates.
- Reduce infant mortality rates.
- Combatting infectious diseases:
- Lower the incidence of death due to TB and HIV/AIDS.
- Reduce the prevalence of HIV and malaria.
- Addressing nutritional deficiencies:
- Decrease anemia prevalence in women of reproductive age.
- Improving healthcare infrastructure:
- Increase the ratio of health professionals (doctors and others) per patient.
- Raise the ratio of primary hospitals per population.
- Expand community health insurance coverage.
- Increasing overall lifespan:
- Raise average life expectancy.
To accomplish these healthcare service delivery improvement targets, adequate number of safe and quality medical devices are constantly required.
In addition to the national generic development plan that has health services improvement plans in it, the Ethiopian Ministry of Health (MoH) has been also implementing the Health Sector Transformation plan (HSTPs) by dividing them into 5-years plans (from 2014/15- 2019/2020 and 2020/2021-2024/25) containing very important strategies in ensuring access to affordable, safe and quality healthcare services. During the HSTP-I period (2014/15–2019/20), the country made significant strides in reducing infant and maternal mortality rates, reflecting the effectiveness of these strategic initiatives.
Ethiopia has been implementing HSTP-II (2021–2025) in response to the evolving socio-economic landscape. This plan is designed to propel the nation towards achieving the universal health coverage (UHC), ultimately leading to improved population health outcomes. The Ministry of Health plays a pivotal role in this process by formulating national health policies, strategies, and guidelines in collaboration with regional health bureaus (RHBs) operating within decentralized administrative structures across the country. In addition to the MoH’s central role, the Ethiopian Food and Drug Authority (EFDA), research institutions like the Ethiopian Public Health Institute (EPHI), and government procurement agencies such as- Ethiopian Pharmaceuticals Supply Service (EPSS) work together to support the successful implementation of healthcare policies and programs. This collaborative approach ensures effective supervision, regulation, and delivery of healthcare services to meet the diverse needs of Ethiopia’s population in terms of access to safe and quality healthcare services.
As Ethiopia continues to implement its comprehensive healthcare plans and strategies, the country is poised to make further advancements in achieving its healthcare objectives, driving positive health outcomes for its citizens and contributing to the overall development and well-being of the nation.
2. Dramatic increase in healthcare facilities and services
Diving into the heart of Ethiopia’s healthcare sector reveals a well-structured three-tier delivery system that plays a pivotal role in catering to the diverse healthcare needs of the population. At the forefront of this system lies the primary level, which encompasses primary healthcare units (PHCUs) (such as health posts, health centers), and primary hospitals. Moving up the ladder, secondary-level services are provided by general hospitals, while specialized hospitals stand ready to offer tertiary care services. These healthcare facilities groups have the capacity of treating large number of patients required from them by their relevant national standards. All these facilities require safe and quality medical devices and IVDs to operate to the required level of standards. This brings big opportunities to the manufacturers of medical devices to market their products in the country. The Ethiopian government is prioritizing healthcare development with increased funding for healthcare service providing institutions. In line with the government’s commitment to enhancing public health services, healthcare infrastructure is being expanded. This includes building new facilities, particularly in rural areas, significantly increasing access to healthcare for all citizens.
The following table shows the total number of healthcare facilities including clinics. This data is up to date and is taken from the Ethiopian Ministry of Health’s live database as of May 20, 2024.
Table 1: Ethiopian Healthcare Facilities, types and numbers, Updated as of May 2024
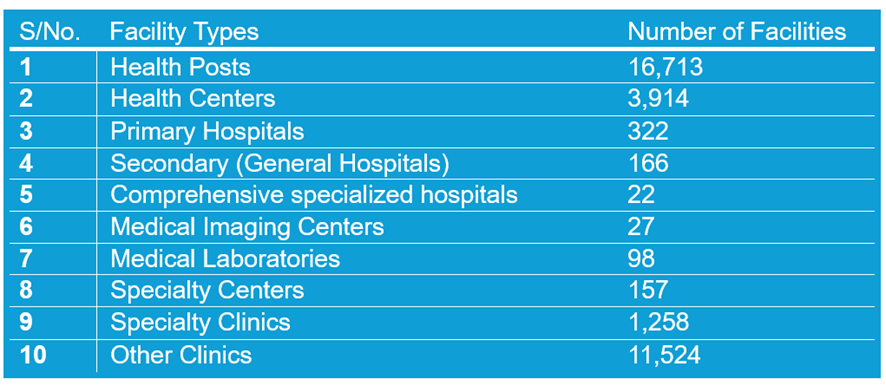
The current landscape of primary care in Ethiopia showcases a network comprising 322 primary hospitals, 3,914 health centers, and 16,713 health posts. These facilities serve as the cornerstone of primary healthcare delivery in the country, ensuring that essential services are accessible and readily available to communities across varied regions.
Within this framework, primary healthcare administration thrives, and primary services are seamlessly facilitated under the structured health service delivery system. As Ethiopia continues its journey towards bolstering its healthcare infrastructure and expanding access to quality services, the three-tier healthcare system stands as a testament to the nation’s commitment to ensuring equitable and efficient healthcare for all its citizens.
3. Population and economic growth thereby leading to higher demand for healthcare services
The macroeconomic factors have played a significant role in propelling the market growth including medical devices market in Ethiopia. The country’s sustained economic growth over the past decade has led to a rise in healthcare spending. Ethiopia’s economy is constantly growing and is currently one of the largest economies in Africa. This rise is driving demand for better healthcare service options.
Local circumstances unique to Ethiopia, such as increase in population size and an expanding middle class, have contributed to the expansion of the medical devices market. With Ethiopia being the second most populous country in Africa, boasting a population exceeding 120 million, the demand for healthcare services and medical devices is on an upward trajectory. The middle class, in particular, with increased disposable income, is willing to invest in better healthcare options, including advanced medical devices.
4. Increasing prevalence of chronic and many infectious diseases
The rising prevalence of non-communicable diseases, such as cardiovascular diseases and diabetes, has fueled the demand for medical devices that aid in diagnosis, monitoring, and treatment. Furthermore, a growing awareness of the benefits of early detection and preventive healthcare has further spurred the need for advanced medical devices.
Diabetes– Diabetes is becoming increasingly prevalent in Ethiopia, leading to higher demand for diabetes management devices.
Cardiovascular diseases– Cardiovascular diseases are also rising, creating a need for diagnostic and treatment devices.
Cancer– Cancer incidence is increasing, driving demand for chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and other cancer treatment devices.
In addition, significant increase in cases of infectious diseases such as- Tuberculosis, Malaria, Syphilis, H.Pylori, HIV, HVB, HVC and others in the country demand adequate number of devices used in the diagnosis and treatment of the diseases. The need for radiology, orthopedics, surgery, laboratory devices also remain top priority to the healthcare delivery of the Country.
5. Transparent and streamlined regulatory system
The medical products regulation in Ethiopia has its legal foundation in Ethiopian Food and Medicines Administration proclamation 1112/2019, giving the Ethiopian Food and Drug Authority (EFDA) the mandate to enforce the compliance of this proclamation and the regulations and directives under it. Every regulatory requirement proposed/drafted by the Authority goes through a series of public consultations involving customers/applicants in setting those requirements to avoid unnecessary barriers that could deny access to safe and quality medical products. The current structure and governance of the medical device regulatory sector being implemented by EFDA is in line with the recommended principles of good regulatory practices (GRP) that promotes transparency, independence and ensures competencies of staff members who get involved in the medical device regulatory decision-making process. Please refer to the medical device registration process by EFDA for detail understanding of the approach.
The Ethiopian Food and Drug Authority has designed and is implementing different approaches to strategically streamline the regulatory assessment and approval of medical devices including in vitro diagnostic devices (IVDs). Some of these approaches are- separate application route and very simplified registration requirements for low-risk medical devices (Class I/A devices), use of reliance mechanism for devices approved by stringent regulatory authorities and trusted organizations (e.g. WHO prequalified IVDs), fast-track assessment and approval of devices for priority diseases. You can refer to our blog on the low-risk medical devices approval process by EFDA. In addition, EFDA’s effort of ensuring harmonization of its regulatory requirements with internationally accepted standards and guidelines (such as- documents by International Medical Device Regulators Forum, IMDRF) makes Ethiopia a preferred entry point to African market by the manufacturers of medical devices due to this favorable regulatory practice. With this regard, Ethiopia is actively participating in international (through IMDRF) and continental (through African Medical Device Forum, AMDF) forums to avoid divergences in regulatory requirements among countries and promote the convergence by adopting or adapting the regulatory documents and tools developed centrally by these forums and other internationally recognized organizations.
In addition, following the re-structuring of the EFDA, the medical device regulatory sector is effectively performing the regulatory activities and constantly monitoring and improving its services’ efficiency, timelines, transparency, impartiality, and clarity. This gives a great opportunity to owners and marketers of medical devices to enter their products into the country’s market.
6. Emerging Medical Tourism Potential
Ethiopia has developed a 10-year strategic policy aimed at establishing the country as a hub for medical tourism. Arguably, Ethiopia is one of the best medical tour destinations in Africa because of-
Affordable Healthcare– Ethiopia offers cost-effective medical treatment options, attracting medical tourists from neighboring countries.
Specialized cares– The country is developing specialized healthcare services, such as heart surgery, orthopedic care, and ophthalmology.
Improving Infrastructure– Investments in infrastructure are making Ethiopia a more attractive destination for medical tourism.
In summary, by considering Ethiopia as their first entry point, medical device manufacturers can gain a foothold in the African market, leverage the country’s dramatic economic growth and population size, benefit from favorable government policies, and expand their market profits to other African Countries.
Ethiobiomedical works to ensure companies who are interested in registering and marketing their medical devices utilize the appropriate and seamless path to meet their dream. Ethiobiomedical does this by professional handling of marketing authorization and post-registration mandatory activities of the product owners required by the Authority. Please contact us for getting consultancy supports to register your devices in Ethiopia.
